MFS for Water Wave Animation
Visual Computing@IST Austria innovated
MFS for Laplace Equation
It is well known that the method of fundamental solutions (MFS) is a numerical method of exponential convergence. In other words, the logarithmic error is proportional to the node number of spatial discretization. In this study, the exponential convergence of MFS is demonstrated by solving Laplace equation in domains of rectangles, ellipses, amoeba-like shapes, and rectangular cuboids. In the solution procedure, the sources of the MFS are located as far as possible and the instability resulted from the ill-conditioning of system matrix is avoided by using the multiple precision floating-point reliable (MPFR) library. The results converge faster for the cases of smoother boundary conditions and larger area/perimeter ratios. The computation is scalable in the sense that the required time increases only algebraically. (Tsai and Lin, 2013)



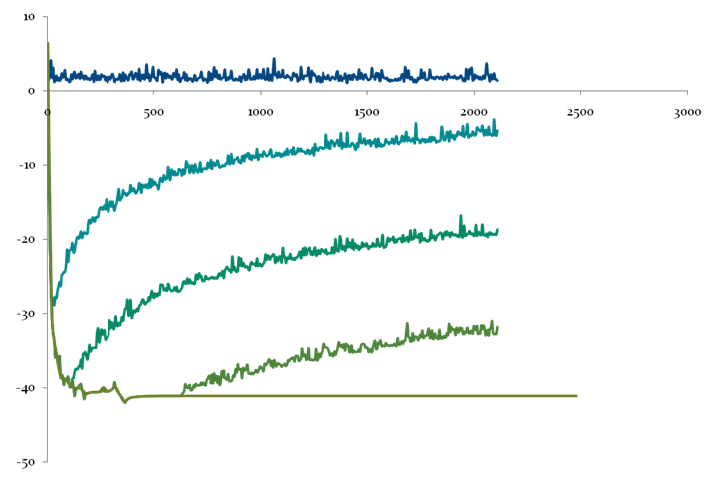
MFS for Helmholtz Eigensolution
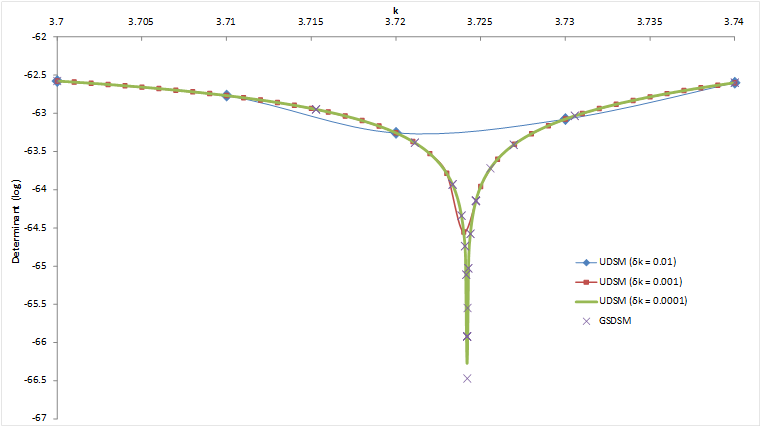
In this study, the exponential convergence of the MFS is demonstrated by obtaining the eigensolutions of Helmholtz equation. In the solution procedure, the sought solution is approximated by a superposition of the Helmholtz fundamental solutions and a system matrix is resulted after imposing the boundary condition. A golden section determinant search method is applied to the matrix for finding exponentially convergent eigenfrequencies. In addition, the least-square method of fundamental solutions is applied for solving the corresponding eigenfunctions. (Tsai and Young, 2013)
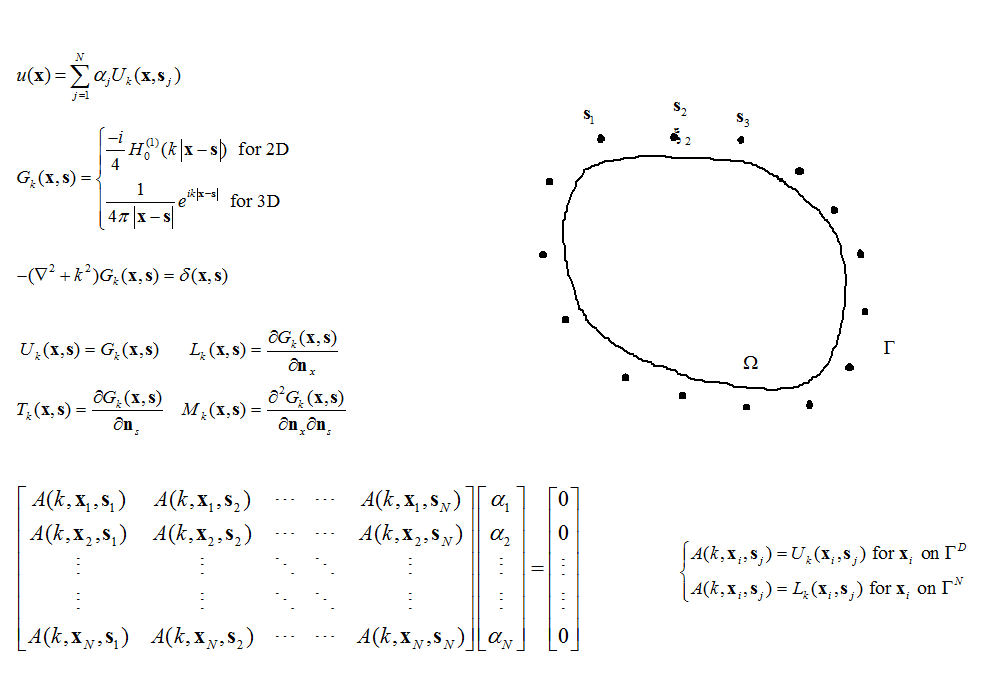
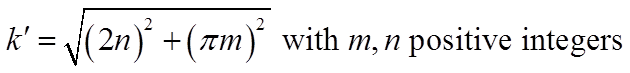
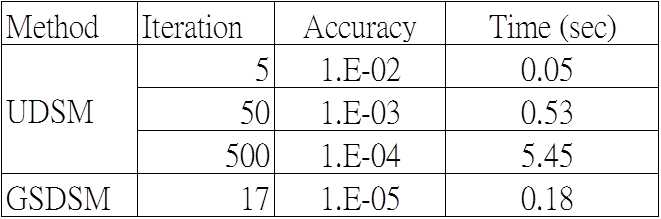


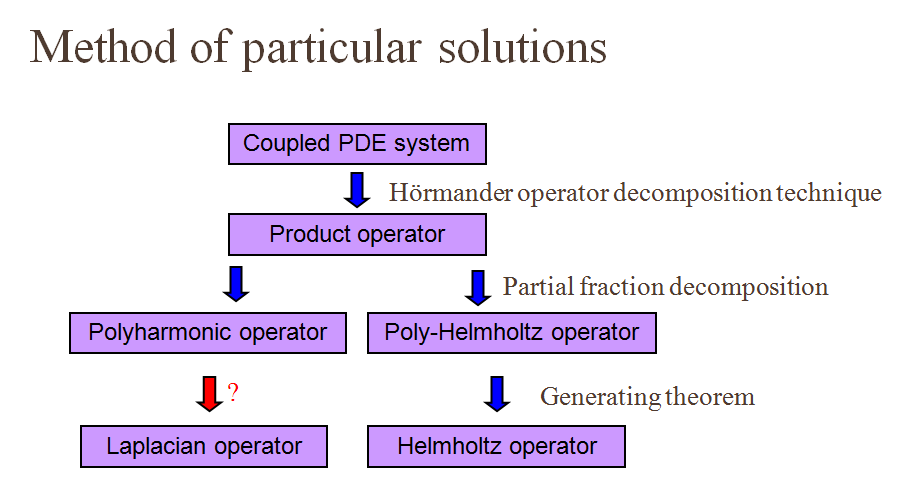
Particular Solutions of Splines and Monomials for Polyharmonic and Products of Helmholtz Operators
This study presents the particular solutions for the polyharmonic and the products of Helmholtz partial differential operators with polyharmonic splines and monomials right hand side. By the application of the Hörmander linear partial differential operator theory, many of the systems can be reduced to a single equation involving the polyharmonic or the product of Helmholtz differential operators. If the inhomogeneous right hand side of these operators can be removed by the method of particular solutions, then boundary-type numerical methods, such as the boundary element method, the method of fundamental solutions, and the Trefftz method, can be applied to solve these differential equations. (Tsai et al., 2009; Tsai, 2011)


Lars Valter Hörmander (24 January 1931 – 25 November 2012), Fields Medal (1962)

Reference
Chia-Cheng Tsai, A.H.-D. Cheng and C.S. Chen (2009, Apr). Particular solutions of splines and monomials for polyharmonic and products of Helmholtz operators. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 33(4), 514-521. Chia-Cheng Tsai (2011, Jul). Automatic particular solutions of arbitrary high-order splines associated with polyharmonic and poly-Helmholtz equations. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 35(7), 925-934.
